과제 1. 문서화
Cookie
cookie: 브라우저에 저장하는 데이터이다. String 형태이며, Key와 Value로 구성된다. 이 데이터가 있는 이유는 HTTP에서 상태를 기억하기 위함이다.
ex) “아이디와 비밀번호를 저장하시겠습니까?”, “오늘 이 창을 다시 보지 않기 - 체크”
cookie 사용 목적
- 세션 관리
- 개인 설정 유지
- 사용자 트래킹: 행동패턴 분석
cookie 구성 요소&동작 방식
이름, 값, 유효시간, 도메인, 경로로 구성되어 있다.
- 사용자가 서버로 요청을 보낸다.
- 서버에서는 쿠키를 들고 응답한다.
- 다시 클라이언트 측에서는 서버로 요청을 보낼 때 쿠키와 함께 보낸다.
- 그럼 서버는 그 쿠키 상태에 맞게 응답한다.
cookie 설정
서버
- HTTP 응답 중 Set-Cookie 추가
- 클라이언트의 브라우저가 Set-cookie한다.
name=test;
클라이언트
자바스크립트로 쿠키를 설정한다.
document.cookie="name=test;"
Session
session: 일정 시간 동안 사용자의 요구를 하나의 상태로 인식하고 유지시키는 기술
쿠키의 보안 취약점을 보완하기 위해서 생긴 개념이다. 쿠키에도 인증 상태를 저장할 수는 있지만 클라이언트가 변조할 수 없도록 세션이 구성되어 있다.
- 클라이언트가 서버에 로그인 요청을 한다.
- 아이디, 비번 일치하면 세션을 생성하여 서버 메모리에 저장한다.
- 서버에서 세션 아이디를 쿠키에 담아 전달한다.
- 클라이언트는 쿠키에 세션아이디 넣어서 다시 서버로 전달한다.
- 서버에서는 세션아이디로 세션을 식별한다.
- 유효하면 서버가 클라이언트에 응답한다.
쿠키와 세션 비교
| cookie | session | |
|---|---|---|
| 저장위치 | 클라이언트 | 서버 |
| 저장형식 | text | object |
| 용량제한 | 도메인 당 20개 1쿠키 당 4kb |
없음 |
| 만료시점 | 쿠키 저장 시 설정 | 알 수 없음 |
| 속도 | 상대적 빠름 | 상대적 느림 |
XSS
Cross Side Scripting: 클라이언트 쪽 취약점, 악성 스크립트 삽입하여 브라우저에서 실행하는 공격
- 공격자가 서버로 악성스크립트 포함한 게시물 전송, 악성스크립트가 포함된 URL 사용자에게 전송
- 사용자가 서버로 요청
- 서버가 응답
- 사용자 PC에서 악성스크립트 실행
Stored XSS
- 악성스크립트 포함된 게시물 서버로 전송
- 악성스크립트가 포함된 게시물(데베에 저장된) 요청
- 응답
- 사용자 PC에서 악성스크립트 실행
Reflected XSS
- 사용자에게 악성스크립트 포함된 URL 전송
- 사용자가 클릭하여 요청
- 응답
- 사용자 PC에서 악성 스크립트 실행
DOM based XSS
문서 객체 모델->브라우저 자체에서 악성 스크립트 실행(서버 상호작용 필요없음)
- DOM: 문서 객체 모델, HTML 문서 읽고 DOM 형태로 재구성해 사용자에게 제공할 때 쓰임
XSS 대응 방안
- 입력값 제한 : 스크립트 삽입하지 못하게 막기
- 입력값 치환: ASCII 문자-> HTML 문자로 치환
- 스크립트 영역에 출력 자제: 핸들러 영역에 스크립트 삽입중에 보호기법 우회를 방지하기 위함
과제 2. cookie 라이트업

#!/usr/bin/python3
from flask import Flask, request, render_template, make_response, redirect, url_for
app = Flask(__name__)
try:
FLAG = open('./flag.txt', 'r').read()
except:
FLAG = '[**FLAG**]'
users = {
'guest': 'guest',
'admin': FLAG
}
@app.route('/')
def index():
username = request.cookies.get('username', None)
if username:
return render_template('index.html', text=f'Hello {username}, {"flag is " + FLAG if username == "admin" else "you are not admin"}')
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('login.html')
elif request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form.get('username')
password = request.form.get('password')
try:
pw = users[username]
except:
return '<script>alert("not found user");history.go(-1);</script>'
if pw == password:
resp = make_response(redirect(url_for('index')) )
resp.set_cookie('username', username)
return resp
return '<script>alert("wrong password");history.go(-1);</script>'
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)
첫 화면

계정은 저렇게 저장되어 있다 admin의 비밀번호를 알 수 없어서 guest로 로그인 했다
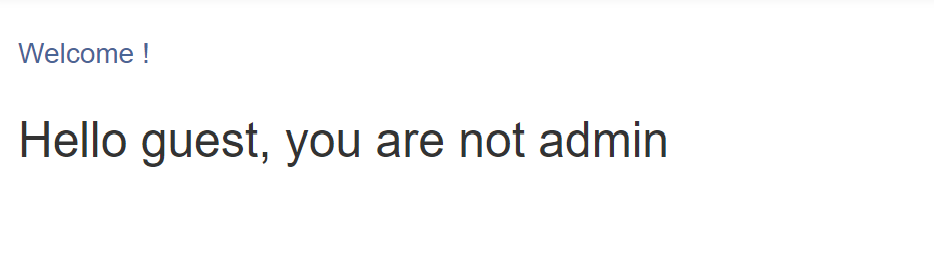
guest 로그인 후 첫 화면
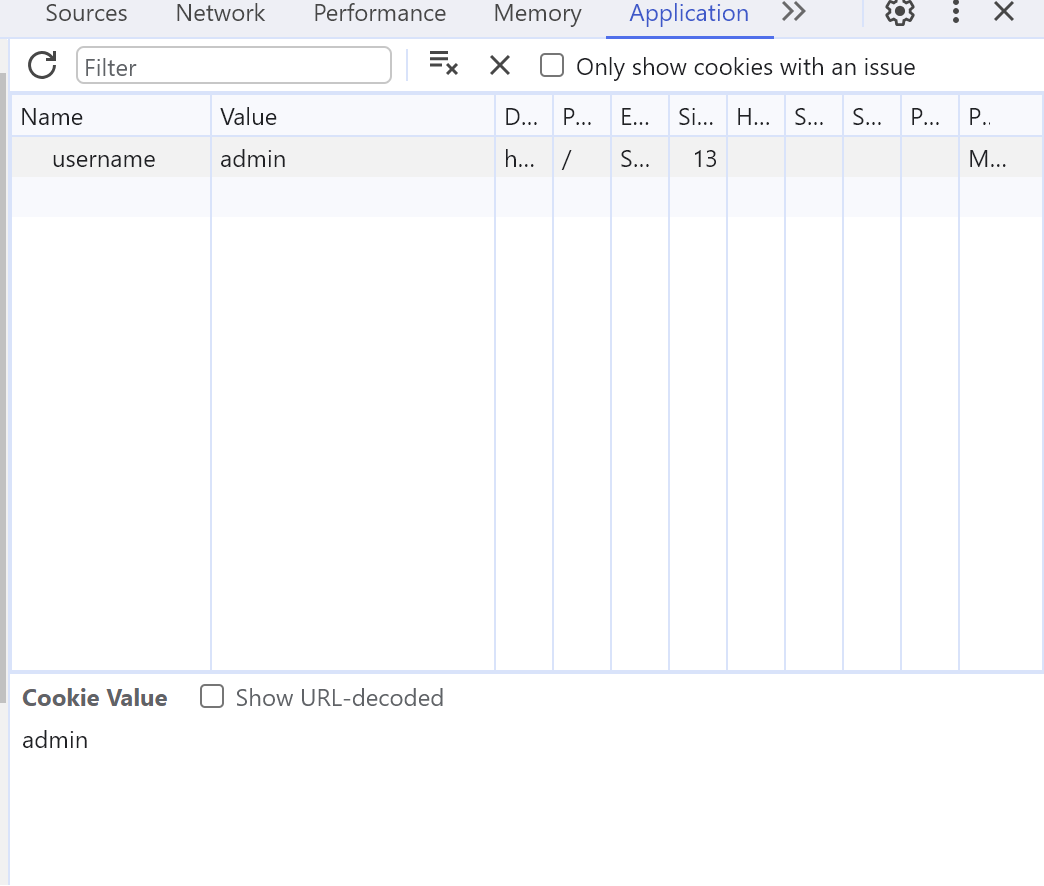
f12 누르기 > application -> cookie 누르면 cookie를 볼 수 있다. session은 없어서 그냥 value를 admin으로 수정했다.
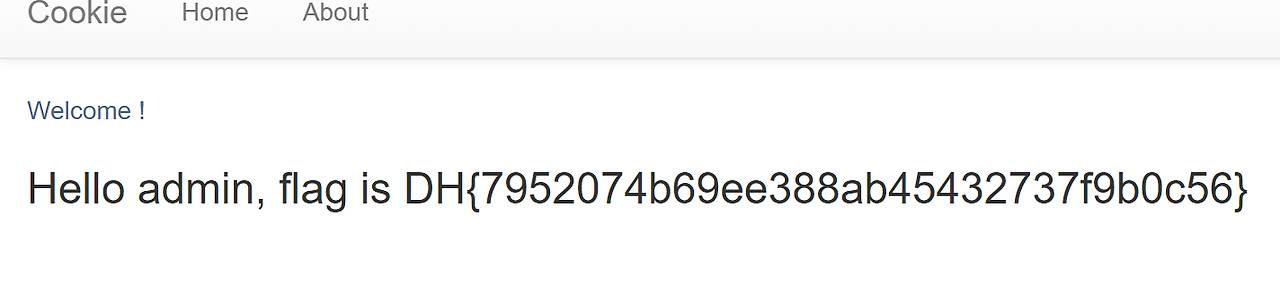
flag 얻기 성공
과제 3. session-basic 라이트업

#!/usr/bin/python3
from flask import Flask, request, render_template, make_response, redirect, url_for
app = Flask(__name__)
try:
FLAG = open('./flag.txt', 'r').read()
except:
FLAG = '[**FLAG**]'
users = {
'guest': 'guest',
'user': 'user1234',
'admin': FLAG
}
# this is our session storage
session_storage = {
}
@app.route('/')
def index():
session_id = request.cookies.get('sessionid', None)
try:
# get username from session_storage
username = session_storage[session_id]
except KeyError:
return render_template('index.html')
return render_template('index.html', text=f'Hello {username}, {"flag is " + FLAG if username == "admin" else "you are not admin"}')
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('login.html')
elif request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form.get('username')
password = request.form.get('password')
try:
# you cannot know admin's pw
pw = users[username]
except:
return '<script>alert("not found user");history.go(-1);</script>'
if pw == password:
resp = make_response(redirect(url_for('index')) )
session_id = os.urandom(32).hex()
session_storage[session_id] = username
resp.set_cookie('sessionid', session_id)
return resp
return '<script>alert("wrong password");history.go(-1);</script>'
@app.route('/admin')
def admin():
# developer's note: review below commented code and uncomment it (TODO)
#session_id = request.cookies.get('sessionid', None)
#username = session_storage[session_id]
#if username != 'admin':
# return render_template('index.html')
return session_storage
if __name__ == '__main__':
import os
# create admin sessionid and save it to our storage
# and also you cannot reveal admin's sesseionid by brute forcing!!! haha
session_storage[os.urandom(32).hex()] = 'admin'
print(session_storage)
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8000)
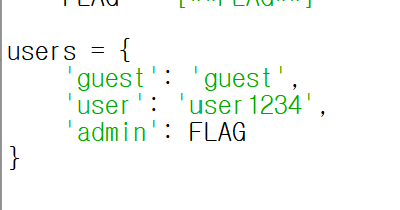
이번에도 계정 먼저 확인했다.
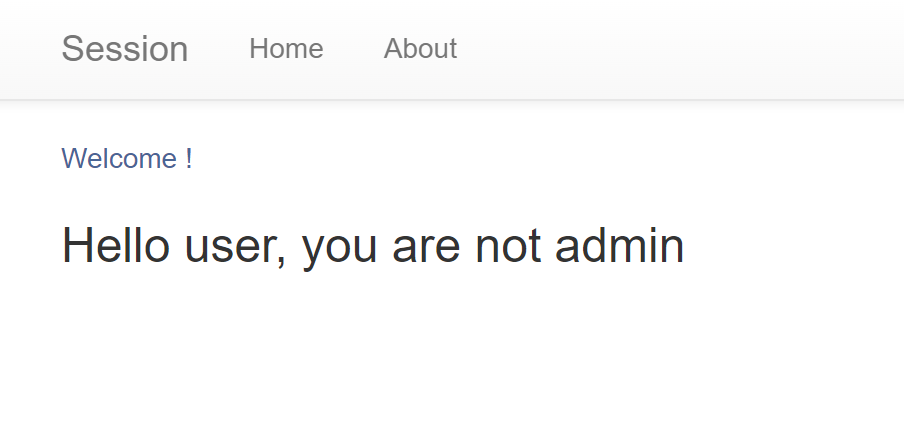
user 로그인 첫화면
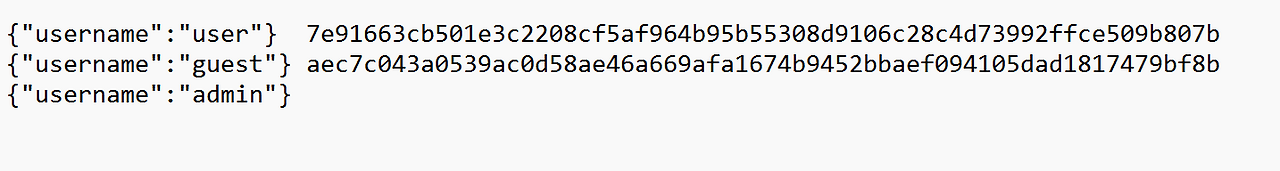
각각의 세션 아이디 os.urandom이라 뭔가를 조합할 수는 없었다(진짜 랜덤)
…모르겠어서 다른 라이트업 참고했다

/admin이라는 숨겨진 부분이 있었다
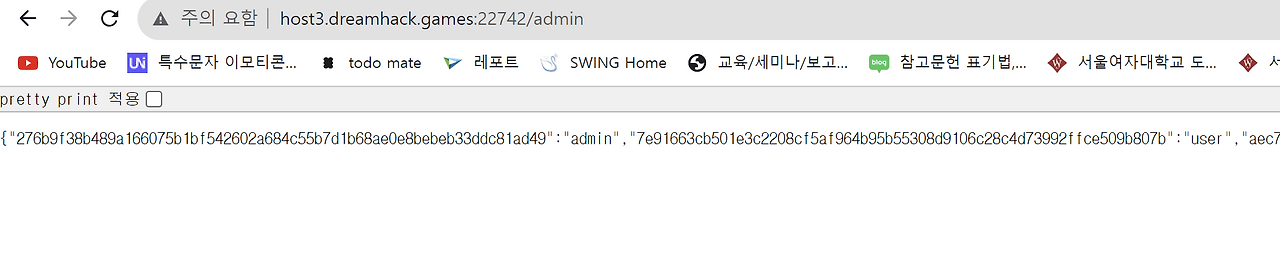
접속하면 session_storage가 반환된다
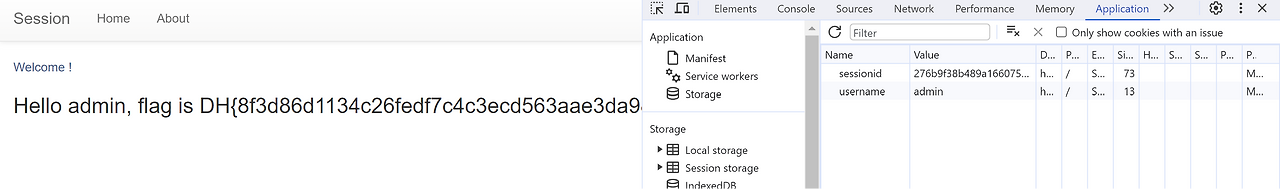
admin에 맞는 세션id 수정하면 플래그가 나온다